A systems-based approach to emergency response means that the disparate elements that are required to perform response operations are viewed as interrelated components of a single system. This is relevant to Healthcare Coalitions since they may involve different organizations working together to achieve a common goal (see Chapter 5). A systems-based approach uses a standardized set of management steps that are sequential and may be applied to any major undertaking.[5] This dictates that overarching objectives, strategies, and tactics are established to promote effective response management and consistency.[6]
The following sections relate how this management methodology might be applied during the initial development of a Healthcare Coalition’s Emergency Operations Plan (EOP). The same methodology might be applied to other major Coalition efforts (e.g., training).
1.2.1 Healthcare Response Goal and Objectives
The application of a systems-based approach for the Healthcare Coalition begins with understanding an overarching goal and supporting objectives for the entire healthcare response – from individual healthcare organizations through local, State, and Federal assistance. An example goal statement and objectives for all levels of MSCC incident response and recovery are stated below.
Goal: To promote healthcare system resiliency and adequate surge capacity and capability across the affected community during a mass casualty and/or mass effect incident.
Objectives to support this goal may include the following:
- Protect healthcare personnel, current patients, visitors, and the integrity of the healthcare system
- Provide the best available medical care for responders, victims, and affected families
- Manage costs, regulatory compliance, and other issues so they do not compromise higher priority objectives
- Develop and use processes that enhance the integration of healthcare organizations into the community response.
1.2.2 Healthcare Response Strategies
Response strategies are established to facilitate achievement of the response goal and objectives. The overarching MSCC priority strategy is presented in Exhibit 1-3. Implementing a Healthcare Coalition, as described in this manual, can be an important step in accomplishing this strategy during emergencies.
Exhibit 1-3. Prioritization of MSCC actions
- Maximize medical surge capability and capacity for individual healthcare organizations (adequate EOP for each medical and healthcare resource).
- Maximize community capacity and capability (situational awareness, mutual aid and other resource sharing arrangements, patient distribution and redistribution, and other support).
- Maximize regional, State, and national capabilities and capacities.
- Institute modified delivery of healthcare to maintain critical medical services.
1.2.3 Healthcare Response as an Overarching System
Using the ICS and Multiagency Coordination principles described in NIMS, the six-tier MSCC model was developed to incorporate the preceding goal, objectives, and strategies for optimal healthcare system resiliency and medical surge.
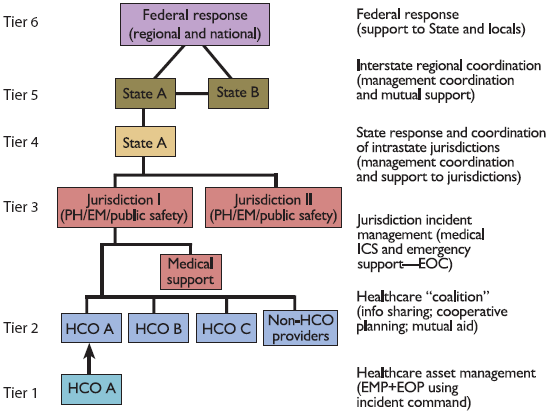
The tiered model presented in the MSCC Handbook (see Figure 1-1 below) demonstrates the relational arrangement of individual healthcare response assets within the local, State, regional, and Federal government construct. Each tier is summarized below.
Tier 1: Encompasses all individual healthcare organizations in a geographic area that deliver “point of service” medical care during emergencies or disasters.
Tier 2: Tier 1 assets that have formed a Healthcare Coalition to share incident information, exchange resource status information that supports mutual aid, coordinate response strategies and tactics, and use a common interface with local jurisdictional authorities to exchange information and request assistance.
Tier 3: Municipal, county, or similar agencies with jurisdiction over the impacted areas and responsibility for the local government response. They are referred to as “Jurisdictional Agencies” throughout this handbook.
Tier 4: State-level response that supports Tiers 1-3 by managing statewide and sub-State regional coordination of the healthcare response.
Tier 5: State-level response that manages inter-State regional coordination of response to support Tiers 1-3 healthcare response assets.
Tier 6: Federal assistance to State, Tribal, local, and non-governmental healthcare response at Tiers 1-5, as managed through a Joint Field Office and/or other Federal coordinating center.
| Figure 1-1. MSCC Management Organization Strategy |
The tiered model demonstrates the relational arrangement of individual healthcare response assets within the local, State, regional, and Federal government construct. It is described in the preceding paragraph.
|
|
|
- Barbera JA, Macintyre AG, Shaw G, et al, Emergency Management Principles and Practices for Healthcare Systems (2006); Available at: www1.va.gov/emshg/page.cfm?pg=122.
- Chapter 5 provides more detail on applying a systems-based approach during design and implementation of a Healthcare Coalition.
<< Previous - Return to Top - Next >>
