Gel-based dressing from patient’s own blood could improve healing after nuclear emergency
Date: September 17, 2013
Company: Arteriocyte Inc. of Cleveland, Ohio
Contract amount: $11.8 million for the first two years of the contract. If milestones are met, the contract can be extended for a total of up to five years and $101 million.
| About this contract: Under today’s contract, Arteriocyte’s novel gel-based dressing Bio-Bandage will be studied for use on severe thermal burn injuries to enhance and accelerate recovery when used in combination with other available treatments after a radiological or nuclear emergency.
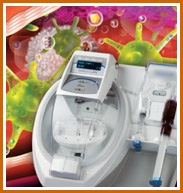
Currently Bio-Bandage is used in medical treatments to heal hip-bone injuries and sternum repairs post surgery as well as in cosmetic surgery. Bio-Bandage is a platelet-rich plasma manufactured from the patient’s own blood using Arteriocyte’s Magellan System. The system is an FDA 510(k)-cleared medical device available commercially and used in thousands of elective procedures each year in hospitals across United States. |
|
In later phases of the project, the company may test the product in larger clinical trials to demonstrate its efficacy, test the product in non-clinical trials for treating burn injuries that occur along with radiation exposure, and will explore how to use the product to lower the total cost of burn care after a radiological or nuclear emergency.
The project is part of a broader BARDA effort to develop products for thermal burn injuries and repurpose existing products for new mass casualty indications. This line of product development is the latest in BARDA’s portfolio of advanced research and development projects for emergency medical countermeasures to treat acute radiation syndrome resulting from bone marrow, lung, gastrointestinal and skin injuries caused by damaging levels of radiation.
In a radiological or nuclear emergency, people are likely to have combined injuries involving trauma, radiation, and thermal burns. The detonation of a nuclear bomb or improvised nuclear device produces intense heat, potentially resulting in severe burns that can cover large portions of a patient’s body. Such thermal burns typically require specialized treatment, including surgical intervention to remove burned tissue and apply skin grafts to the resulting wound bed over weeks or months.
BARDA supports the development of many of the products that may find uses beyond disasters response, especially in the case of severe thermal burns. Where possible, BARDA seeks to enhance preparedness for public health emergencies by supporting the development of products that also address other unmet medical needs.
